Arctic Oil spill
20,000 tonnes of stored diesel leaked into a river when a tank at a power plant near the city of Norilsk collapsed on May 29, 2020. Norilsk is known as Russia’s nickel capital. Norilsk Nickel is also the world’s largest palladium producer and a leading producer of nickel, platinum, and copper.
Reason
Initial Russian inquiries suggest ground subsidence as the reason. The thermoelectric power station at Norilsk is constructed on permafrost. Permafrost has weakened over the years owing to climate change. This caused the sinking of the pillars which supported the fuel tank of the plant.
Impact
Reports said that leaked oil drifted some 12km from the site, turning long stretches of the Ambarnaya river crimson red. A World Wildlife Fund speaking to the AFP news agency expressed this as the second-biggest known oil leak in modern Russia’s history in terms of volume. The leak in the Ambarnaya river has endangered local ecology. This forced the Russian government to impose an emergency in the area along the Ambarnaya river.
Role of S5P-Tropomi
The scale of Norilsk’s pollution problem is captured in extraordinary new maps from Europe’s Sentinel-5P satellite. The SO₂ concentrations in the air above Norilsk are very large. Satellites such as S5P-Tropomi are making it increasingly difficult for polluters to conceal their activity.
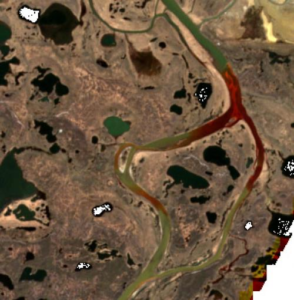
Photo: Satellite picture from Sentinel-2 / WWF Russia
Definition of oil spill
Oil spills are leakages or spillage of petroleum and its byproducts into the environment particularly onto the surface of huge water bodies such as oceans, lakes, and rivers. It is principally applied to describe the spillage of oil in marine systems. However, oil spills may occur on land too.
Recent oil spills in India
The most disastrous oil spills in India include the following accidents-
- 2017- Ennore oil spill due to collision between the LPG tanker and oil tanker
- 2014- Oil spill in Bangladesh. However, this affected the Sundarban of West Bengal.
- 2013- ONGC Oil spill in Mumbai (Arabian sea)
- 2010- On Mumbai coast
THREAT OF SPILLS
India is the second-biggest consumer of oil equivalent primary energy in the Asia-Pacific region after China. Around 70% of the global oil demand is ferried along the Indian coastline. More than 7,000 POL tankers are handled annually from major ports in India. This puts the country at risk from oil spills.
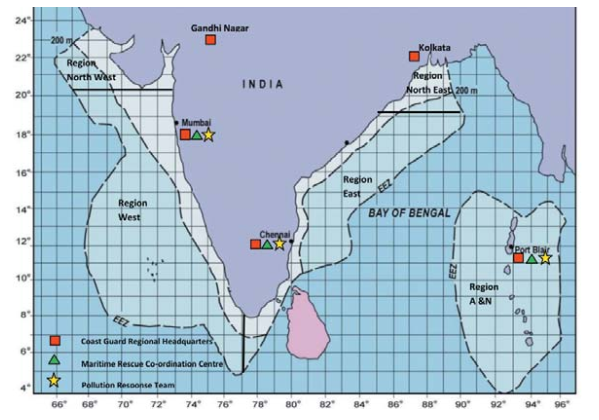
High Seas where an oil or chemical spill has the potential to impact on Indian interests in the maritime zones of India
Reasons
-
Natural disasters like heavy storms in the oceans, hurricanes, and shaking of the seafloor due to earthquakes, Eg. 1992 oil spill of La Coruña in Spain
-
Marine accidents due to natural disasters
-
Increased deep-sea oil production and explorations
-
Mechanical breakdown or malfunction of the oil drilling machinery
-
Deliberate acts by terrorists, vandals, or countries at war Eg. Gulf War oil spill
-
Illegal dumping of used oil in inland areas
-
The transportation of crude oil over the seas by use of voluminous tankers
Consequences
Environment
- When an oil spill occurs at sea, oil floats over the water since it is lighter. Thus, it catches fire swiftly and endangers the ecosystem for all times.
- Oil spills on land can also cause fire hazards and pollute groundwater and air.
- It causes serious harm to marine mammals, birds, sea otters, shellfish, and sea coral. The oils interfere with the insulating ability of mammals with furs resulting in restriction of movement, asphyxia.
- Approximately one million seabirds of the coast, 5,000 marine mammals, and 1,000 sea turtles were killed by the explosion in 2010 by BP’s Deepwater Horizon rig in the Gulf of Mexico.

Oiled Bird – Black Sea Oil Spill
- The contaminated waters result in a sharp drop in the diversity of phytoplankton and zooplankton. This is because oil inhibits sunlight penetration into the water which affects photosynthesis and food production by the phytoplankton.
- Both the global food chain and the world’s waters are being gradually poisoned by all of this oil. It results in bioaccumulation and biomagnification of poisonous substances in the food chain.
- Long-term ecological impacts of oil and chemical-
– Affects animals’ liver, kidney, spleen, brain or other organs
– Cause cancer, immune system suppression, and reproductive failure
– Trigger long-term environmental changes by damaging animals’ nesting or breeding grounds.
Socio-economic
- Oil spills can cause serious damage to Fishing, shrimping, and oyster industries. In turn, it affects the jobs and earnings of fishermen and shrimpers.
- It affects tourism and recreational activities such as swimming, boating. Wide-scale pollution may change public perception and tourists may prefer other destinations. It surely affects local tourism-dependent businesses.
- Oil Spills have a dramatic chilling effect on oil exploration. Such disasters slow the exploration and development of offshore oil projects worldwide due to delayed environment clearance, less inclination of investors towards oil exploration, and demonstration by locals against future projects.
- Big oil spills may disrupt the supply of oil resulting in a rise in oil prices worldwide.
Human Health
- While cleaning up oil products from the water surface or the shoreline without precautions may result in inhaling vapors from oils, skin contact with the oil. It may cause skin and eye irritation, neurologic and breathing problems, and stress.
- Concentrations of petroleum contaminants in fish and crab tissue, as well as contamination of shellfish, could have a significant potential for adverse human health effects including damage to the nervous, immune, and reproductive system.
Management issues
- Coordinated efforts to clean up the spill are still lacking, especially in developing countries.
- In India, there is no separate law covering the oil spill and its impacts on ecology and human health. These incidents are covered as an accidental discharge as defined in the Environment Protection Act (EPA) of 1986.
National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOS-DCP)
- India is a party to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and has the duty to protect and conserve the marine environment.
- The responsibility for the co-ordination of marine oil spills at sea was transferred to the Coast Guard from the Directorate General of Shipping on in 1986. Consequent to the transfer of responsibility, a draft National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOS-DCP) was drawn up by the Coast Guard.
The NOS-DCP has been in operation since July 1996 and pools the combined resources of:
- the Government of India including that of the Indian Coast Guard
- the State Governments including emergency services; and
- the shipping, ports, and oil industries.
Solutions
- “Natural recovery” is an important component. Wave action, naturally occurring microorganisms, sunlight, and dispersion of natural water contribute to breaking down oil leaked into the ocean.
- Traditional methods involve breaking up the oil with dispersants or skimming it off the surface, manual or mechanical cleanup. However, those methods are expensive, slow, and unsafe.
- Sorbent materials like straw, clay, sand, etc. can be used. These materials are cheap and available in large quantities. However, they are most frequently used in small spills or to remove the final traces of a large spill.
- Marsh cleans up techniques can be employed. It includes vacuum pumping, low-pressure flush.
- Hay, Oil spill hair mats, oil-eating mushrooms, Pine shavings, beeswax can also be used.
Technological solutions
- Oil Zapper and Nanosheets has the potential to revolutionalize oil spills management.
- Oilzapper is a bacterial consortium that degrades crude oil and oily sludge. The Oilzapper feeds on compounds of hydrocarbon found in crude oil and oily sludge and converts them into harmless CO2 and water. This is called bioremediation. It was used to clean up the Mumbai shoreline hit by the oil spill that occurred in August 2010.
- As per scientists claim, nanosheets can absorb 33 times their weight in oil, they’re also recyclable.
It is important that we understand the environmental implications of oil spills and raise awareness to prevent future catastrophes. Many of the effects are long-lasting and irreversible.
You can also read-

Nice content… Keep it up
Thank you very much…